HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It is a standard markup language for web page creation. It allows the creation and structure of sections, paragraphs, and links using HTML elements (the building blocks of a web page) such as tags and attributes.It is used to align the content in sementic way by wrapping, which is useful in css to add styles and designs. It is static web page.
With HTML you can create your own Website.
HTML is easy to learn - You will enjoy it!
HTML is the only markup language available to structure a webpage , so thats why we are using html, without creating this we can't make a web page.
Right now we are using html 5.
we are going to see the difference between html and html 5 in this page. first we used html to make webpages, after that we got a browser and advanced technologies so we have to update the html aswell for the usage. so we built new things to use in html 5. we are going to see the difference between them in a table here and also we are going to see about meta characters in head and their uses and interview questions.
| HTML | HTML 5 |
|---|---|
| we use docutype to tell the browser what type of document we are using, and browser use doctype to render the html. it is very long here. we have to enter like this, !doctype HTML PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01//EN""http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/strict.dtd" | In html 5 we simplify the doctype, so its easy to remember and it no longer references a dtd. it changed to this method !doctype html |
| it has very less input types to use in a form, so its hard for the user. | In html 5 we add lot of new input types for the user experience. for ex: email, range, tel, url, number,date , datetime, datetime-local, colour, search |
| it don't have a video and audio inputs | it has a audio and video controls |
| no sementic elements used, only have div | Includes sementic elements for a better structure and understanding for the browser |
| No specific support for mobiles mobile friendly to use , we can use in any device. | mobile friendly to use , we can use in any device |
HTML
Head & Body
Inside the body and inside the block level element
Element is described as the opening tag and closing tag including the content inside the tag, alltogether called as a element.
We have two types of elements.
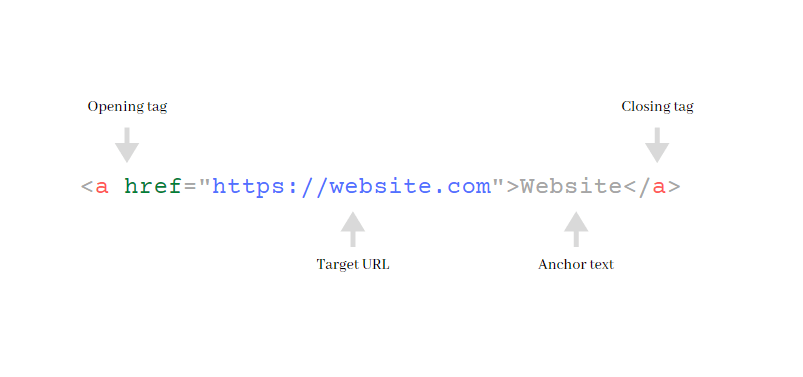
| href: | we use this inside the anchor tag to provide url for the anchor tag. |
|---|---|
| <a href="index.html">IT magic</a> | |
| src: | we use this inside the image tag to provide source of the image. |
| <img src="htmlimages/image"/> | |
| alt: | we use this inside the image tag to provide the description of the image if it is failed to load on the webpage. |
| <img src="htmlimages/image" alt="image"/> | |
| style: | We use this inside the starting tag to give design the element. |
| <h1 style="property:value;"> My web page </h1> | |
We also have a attributes like height, width to edit the sizes.
We have a lot of attributes for form, we will see them all in the form section.